Eavesdropping on Neurons
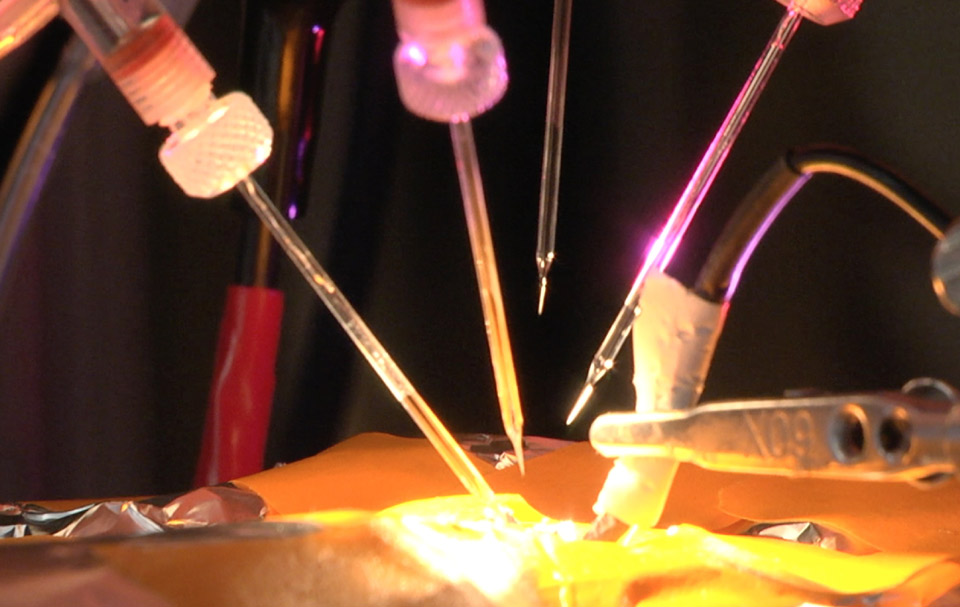
Several new tools for exploring individual neurons allow scientists to probe the workings of the brain in great detail. Optogenetics makes it possible to turn specific neurons on and off in lab animals to determine how those brain cells are affecting activity. Patch clamping lets scientists record the electrical activity of neurons inside a living brain, a process that has now been automated.
Keep Reading
Most Popular
Large language models can do jaw-dropping things. But nobody knows exactly why.
And that's a problem. Figuring it out is one of the biggest scientific puzzles of our time and a crucial step towards controlling more powerful future models.
How scientists traced a mysterious covid case back to six toilets
When wastewater surveillance turns into a hunt for a single infected individual, the ethics get tricky.
The problem with plug-in hybrids? Their drivers.
Plug-in hybrids are often sold as a transition to EVs, but new data from Europe shows we’re still underestimating the emissions they produce.
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from
MIT Technology Review
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.