Limits of climate change
A “stabilizing feedback” mechanism acts to keep global temperatures in check—but not fast enough to help us.
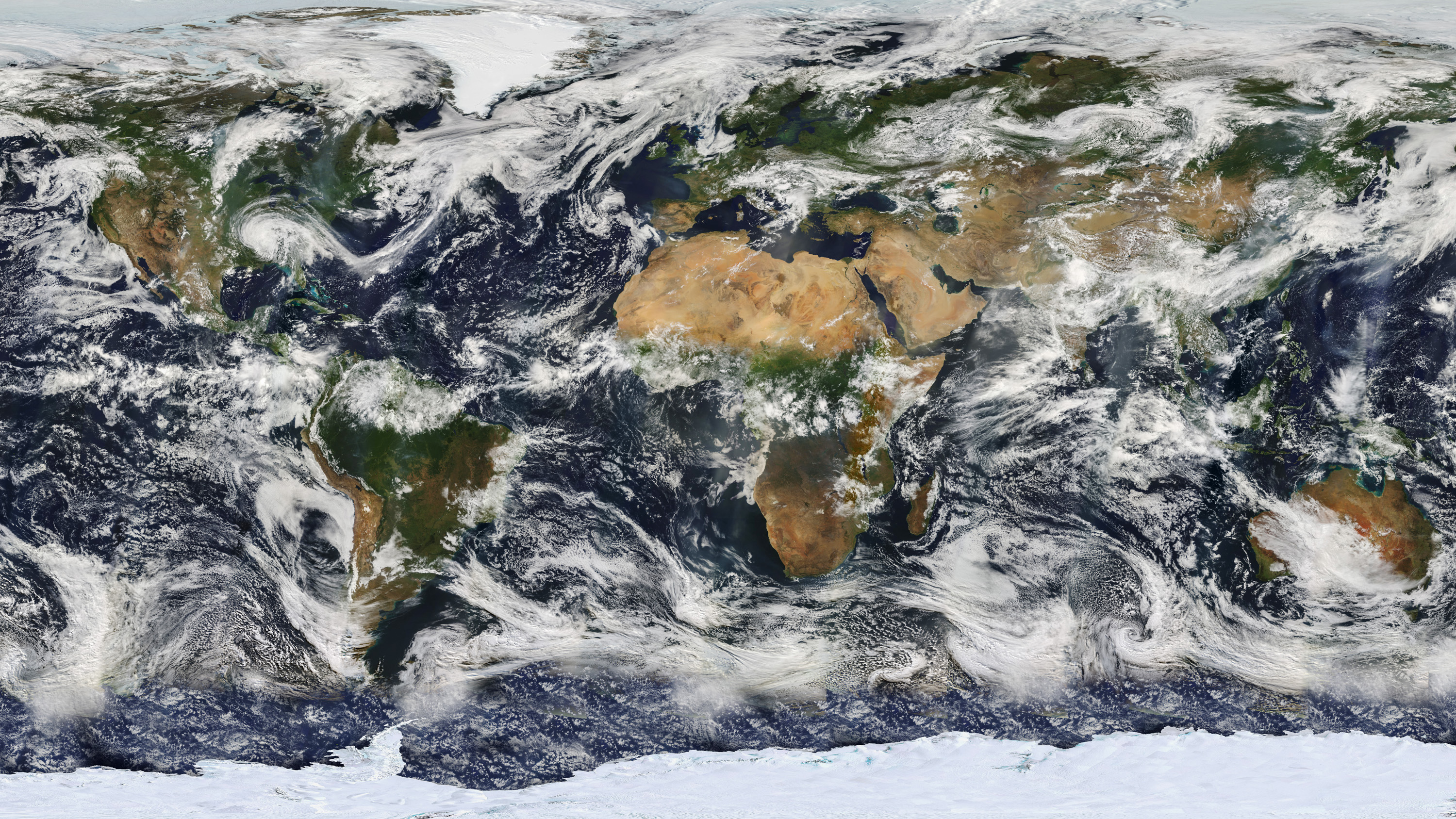
Earth’s climate has undergone some big changes, from global volcanism to planet-cooling ice ages. And yet life, for the last 3.7 billion years, has kept on beating.
Now a study by MIT researchers confirms something long suspected: that a “stabilizing feedback” mechanism keeps global temperatures within a habitable range. The likely key is the slow and steady weathering of silicate rocks, which involves chemical reactions that draw carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere and into ocean sediments.
The researchers applied a mathematical analysis to data that record changes in average global temperatures over the last 66 million years. They found that there appears to be a consistent pattern in which temperature swings are dampened over hundreds of thousands of years, similar to the time scales over which silicate weathering is predicted to act.
“On the one hand, it’s good because we know that today’s global warming will eventually be canceled out through this stabilizing feedback,” says graduate student Constantin Arnscheidt, a coauthor of the study. “But on the other hand, it will take hundreds of thousands of years to happen, so not fast enough to solve our present-day issues.”
Keep Reading
Most Popular
Large language models can do jaw-dropping things. But nobody knows exactly why.
And that's a problem. Figuring it out is one of the biggest scientific puzzles of our time and a crucial step towards controlling more powerful future models.
How scientists traced a mysterious covid case back to six toilets
When wastewater surveillance turns into a hunt for a single infected individual, the ethics get tricky.
The problem with plug-in hybrids? Their drivers.
Plug-in hybrids are often sold as a transition to EVs, but new data from Europe shows we’re still underestimating the emissions they produce.
Google DeepMind’s new generative model makes Super Mario–like games from scratch
Genie learns how to control games by watching hours and hours of video. It could help train next-gen robots too.
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from
MIT Technology Review
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.