Sponsored
These five AI developments will shape 2021 and beyond
Despite the travesties of 2020, artificial intelligence has quickened its progress. Baidu upped its performance across vaccines, autonomous vehicles, language processing, and quantum computing.

Provided byBaidu
The year 2020 was profoundly challenging for citizens, companies, and governments around the world. As covid-19 spread, requiring far-reaching health and safety restrictions, artificial intelligence (AI) applications played a crucial role in saving lives and fostering economic resilience. Research and development (R&D) to enhance core AI capabilities, from autonomous driving and natural language processing to quantum computing, continued unabated.
Baidu was at the forefront of many important AI breakthroughs in 2020. This article outlines five significant advances with implications for combating covid-19 as well as transforming the future of our economies and society.
1. AI and vaccine development
The trend—and why it matters. It typically takes years, if not decades, to develop a new vaccine. But by March 2020, vaccine candidates to fight covid-19 were already undergoing human tests, just three months after the first reported cases. The record speed of vaccine development was partly thanks to AI models that helped researchers analyze vast amounts of data about coronavirus.
There are tens of thousands of subcomponents to the outer proteins of a virus. Machine learning models can sort through this blizzard of data and predict which subcomponents are the most immunogenic—i.e., capable of producing an immune response—and thereby guide researchers in designing targeted vaccines. The use of AI in vaccine development may revolutionize the way all vaccines are created in the future.
Baidu’s innovations. In February, Baidu opened its LinearFold AI algorithm for scientific and medical teams working to fight the virus. LinearFold predicts the secondary structure of the ribonucleic acid (RNA) sequence of a virus—and does so significantly faster than traditional RNA folding algorithms. LinearFold was able to predict the secondary structure of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA sequence in only 27 seconds, 120 times faster than other methods. This is significant, because the key breakthrough of covid-19 vaccines has been the development of messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines. Instead of conventional approaches, which insert a small portion of a virus to trigger a human immune response, mRNA teaches cells how to make a protein that can prompt an immune response, which greatly shortens the time span involved in development and approval.
To support mRNA vaccine development, Baidu later developed and released an AI algorithm for optimizing mRNA sequence design called LinearDesign, which aims to solve the problem of unstable and unproductive mRNA sequences in candidate vaccines.
In addition to opening up access to LinearFold and LinearDesign for researchers around the world, Baidu also formed a strategic partnership with the National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention, part of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Following an outbreak at Beijing’s Xinfadi market in June, Baidu’s AI technology allowed authorities to complete genome sequencing of the coronavirus strain within 10 hours, helping curb the outbreak. In December, Baidu unveiled PaddleHelix, a machine learning-based bio-computing framework aimed at facilitating the development of vaccine design, drug discovery, and precision medicine.
2. Fully automated driving and the rollout of robotaxis
The trend—and why it matters. Autonomous driving technology continued to mature in 2020, with the industry’s leading companies testing driverless cars and opening up robotaxi services to the public in various cities. Fully automated driving, which enables rides without a human safety driver on board, will be necessary for the scalability and commercialization of autonomous driving.
Baidu’s innovations. Over the past year, Baidu launched the Apollo Go Robotaxi service in the Chinese cities of Changsha, Cangzhou, and Beijing—including in busy commercial areas—becoming the only company in China to start robotaxi trial operations in multiple cities.
These developments are a result of Baidu’s continuous innovation in developing AI systems that can safely control a vehicle in complex road conditions and solve the majority of possible issues on the road, independent of a human driver.
At Baidu World 2020, its annual technology conference, Baidu also demonstrated its fully automated driving capability—where the AI system drives independently without an in-vehicle safety driver. To support fully automated driving, Baidu developed the 5G Remote Driving Service, a safety measure whereby remote human operators can take control of a vehicle in the event of an exceptional emergency. Baidu’s achievement of fully automated driving, and the rollout of its robotaxis, suggests a positive outlook for the commercialization of the technology in the near future.

3. Applied natural language processing
The trend—and why it matters. In 2020, natural language systems became significantly more advanced at processing aspects of human language like sentiment and intent, generating language that aligns with human speaking and writing patterns, and even visual understanding, meaning the capability to express understanding about an image through language. These natural language models are powering more accurate search results and more sophisticated chatbots and virtual assistants, leading to better user experiences and creating value for businesses.
Baidu’s innovations. Baidu released a new multiflow sequence framework for language generation called ERNIE-GEN. By training the model to predict semantically complete blocks of text, ERNIE-GEN performs at an elite level across a range of language generation tasks, including dialogue engagement, question generation, and abstractive summarization.
Baidu’s vision-language model ERNIE-ViL also achieved significant progress in visual understanding, ranking first on the VCR leaderboard, a dataset of 290,000 questions built by the University of Washington and the Allen Institute for AI, that aims to test visual understanding ability. ERNIE-ViL also achieved state-of-the-art performance on five vision-language downstream tasks. Visual understanding lays the foundation for computer systems to physically interact in everyday scenes, as it involves both understanding visual content and expressing it through language. It will be crucial for improving the quality of human-machine interaction.
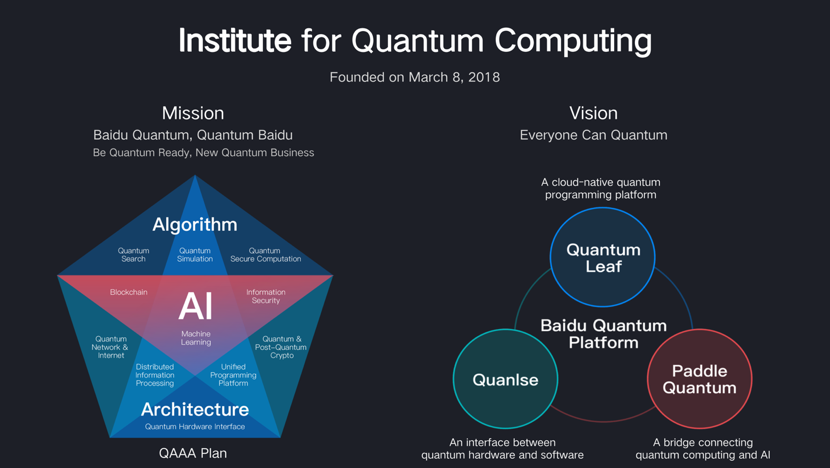
4. Quantum computing
The trend—and why it matters. Quantum computing made significant inroads in 2020, including the Jiuzhang computer’s achievement of quantum supremacy. This carries significance for AI, since quantum computing has the potential to supercharge AI applications compared to binary-based classical computers. For example, quantum computing could be used to run a generative machine learning model through a larger dataset than a classical computer can process, thus making the model more accurate and useful in real-world settings. Advanced technologies such as deep learning algorithms are also playing an increasingly critical role in the development of quantum computing research.
Baidu’s innovations. Baidu achieved a number of technical breakthroughs in 2020 that promise to bridge AI and quantum computing. In May, Baidu launched Paddle Quantum, a quantum machine learning development toolkit that can help scientists and developers quickly build and train quantum neural network models and provide advanced quantum computing applications. The open-source toolkit both supports developers building quantum AI applications, and helps deep learning enthusiasts develop quantum computing. In September, Baidu entered cloud-based quantum computing with the launch of Quantum Leaf, which provides quantum development kits such as QCompute, and can shorten the life cycle of quantum programming and help realize a ‘closed-loop’ quantum tool chain.
5. AI chips
The trend—and why it matters. AI hardware continued to develop in 2020, with the launch of several AI chips customized for specialized tasks. While an ordinary processor is capable of supporting AI tasks, AI-specific processors are modified with particular systems that can optimize performance for tasks like deep learning. As AI applications become more widespread, any increase in performance or reduction in cost can unlock more value for companies that operate a wide network of data centers for commercial cloud services, and can facilitate the company’s internal operations.
Baidu’s innovations. At Baidu World 2020, the company offered a glimpse into its next-generation AI processor, the Kunlun 2, which it plans to put into mass production in early 2021. The chip uses 7 nanometer (nm) processing technology and its maximum computational capability is over three times that of the previous generation, the Kunlun 1. The Kunlun chips are characterized by high performance, low cost, and high flexibility, which can support a broad range of AI applications and scenarios, helping foster greater AI adoption and reducing usage costs. More than 20,000 Kunlun 1 chips have now been deployed to support Baidu’s search engine and Baidu Cloud partners since they launched in 2018, empowering industrial manufacturing, smart cities, smart transportation, and other fields.
This content was produced by Baidu. It was not written by MIT Technology Review’s editorial staff.
Keep Reading
Most Popular
Large language models can do jaw-dropping things. But nobody knows exactly why.
And that's a problem. Figuring it out is one of the biggest scientific puzzles of our time and a crucial step towards controlling more powerful future models.
The problem with plug-in hybrids? Their drivers.
Plug-in hybrids are often sold as a transition to EVs, but new data from Europe shows we’re still underestimating the emissions they produce.
Google DeepMind’s new generative model makes Super Mario–like games from scratch
Genie learns how to control games by watching hours and hours of video. It could help train next-gen robots too.
How scientists traced a mysterious covid case back to six toilets
When wastewater surveillance turns into a hunt for a single infected individual, the ethics get tricky.
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from
MIT Technology Review
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.