Google’s medical AI was super accurate in a lab. Real life was a different story.
The covid-19 pandemic is stretching hospital resources to the breaking point in many countries in the world. It is no surprise that many people hope AI could speed up patient screening and ease the strain on clinical staff. But a study from Google Health—the first to look at the impact of a deep-learning tool in real clinical settings—reveals that even the most accurate AIs can actually make things worse if not tailored to the clinical environments in which they will work.
Existing rules for deploying AI in clinical settings, such as the standards for FDA clearance in the US or a CE mark in Europe, focus primarily on accuracy. There are no explicit requirements that an AI must improve the outcome for patients, largely because such trials have not yet run. But that needs to change, says Emma Beede, a UX researcher at Google Health: “We have to understand how AI tools are going to work for people in context—especially in health care—before they’re widely deployed.”
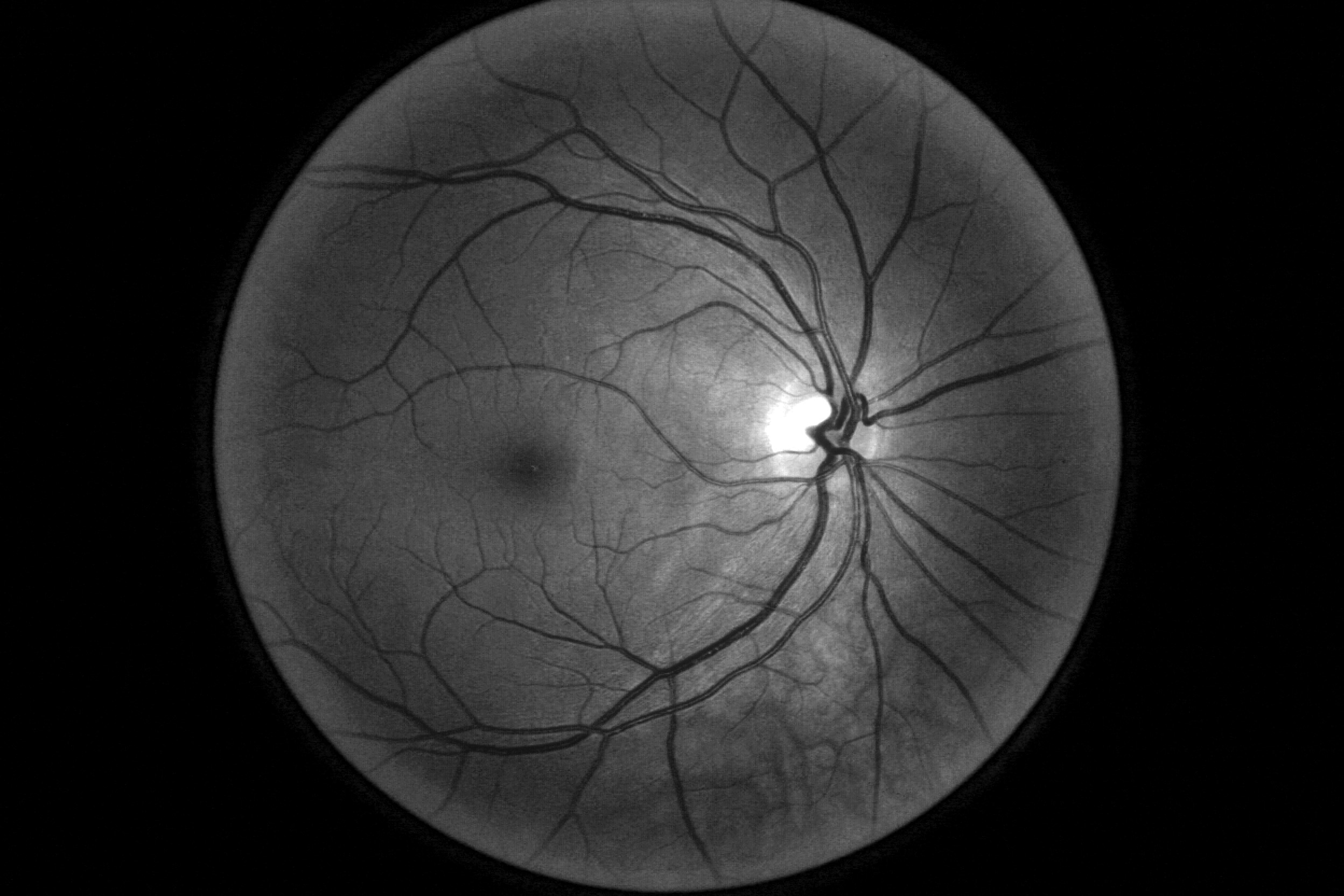
Google’s first opportunity to test the tool in a real setting came from Thailand. The country’s ministry of health has set an annual goal to screen 60% of people with diabetes for diabetic retinopathy, which can cause blindness if not caught early. But with around 4.5 million patients to only 200 retinal specialists—roughly double the ratio in the US—clinics are struggling to meet the target. Google has CE mark clearance, which covers Thailand, but it is still waiting for FDA approval. So to see if AI could help, Beede and her colleagues outfitted 11 clinics across the country with a deep-learning system trained to spot signs of eye disease in patients with diabetes.
In the system Thailand had been using, nurses take photos of patients’ eyes during check-ups and send them off to be looked at by a specialist elsewhere—a process that can take up to 10 weeks. The AI developed by Google Health can identify signs of diabetic retinopathy from an eye scan with more than 90% accuracy—which the team calls “human specialist level”—and, in principle, give a result in less than 10 minutes. The system analyzes images for telltale indicators of the condition, such as blocked or leaking blood vessels.
More on coronavirus
Our most essential coverage of covid-19 is free, including:
How does the coronavirus work?
What are the potential treatments?
What's the right way to do social distancing?
Other frequently asked questions about coronavirus
---
Newsletter: Coronavirus Tech Report
Zoom show: Radio Corona
See also:
Please click here to subscribe and support our non-profit journalism.
Sounds impressive. But an accuracy assessment from a lab goes only so far. It says nothing of how the AI will perform in the chaos of a real-world environment, and this is what the Google Health team wanted to find out. Over several months they observed nurses conducting eye scans and interviewed them about their experiences using the new system. The feedback wasn’t entirely positive.
When it worked well, the AI did speed things up. But it sometimes failed to give a result at all. Like most image recognition systems, the deep-learning model had been trained on high-quality scans; to ensure accuracy, it was designed to reject images that fell below a certain threshold of quality. With nurses scanning dozens of patients an hour and often taking the photos in poor lighting conditions, more than a fifth of the images were rejected.
Patients whose images were kicked out of the system were told they would have to visit a specialist at another clinic on another day. If they found it hard to take time off work or did not have a car, this was obviously inconvenient. Nurses felt frustrated, especially when they believed the rejected scans showed no signs of disease and the follow-up appointments were unnecessary. They sometimes wasted time trying to retake or edit an image that the AI had rejected.
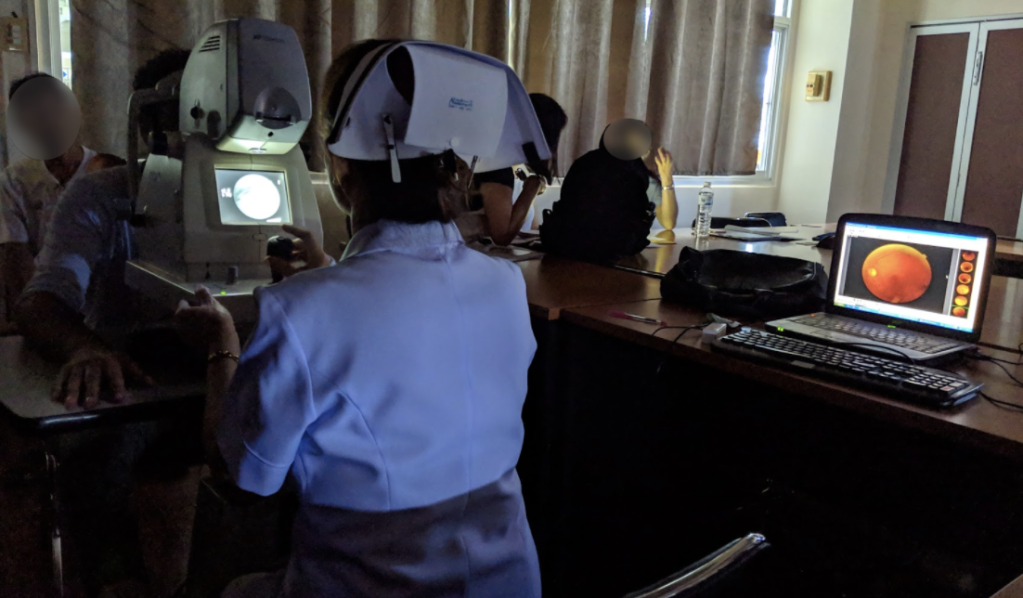

Because the system had to upload images to the cloud for processing, poor internet connections in several clinics also caused delays. “Patients like the instant results, but the internet is slow and patients then complain,” said one nurse. “They’ve been waiting here since 6 a.m., and for the first two hours we could only screen 10 patients.”
The Google Health team is now working with local medical staff to design new workflows. For example, nurses could be trained to use their own judgment in borderline cases. The model itself could also be tweaked to handle imperfect images better.
Risking a backlash
“This is a crucial study for anybody interested in getting their hands dirty and actually implementing AI solutions in real-world settings,” says Hamid Tizhoosh at the University of Waterloo in Canada, who works on AI for medical imaging. Tizhoosh is very critical of what he sees as a rush to announce new AI tools in response to covid-19. In some cases tools are developed and models released by teams with no health-care expertise, he says. He sees the Google study as a timely reminder that establishing accuracy in a lab is just the first step.
Michael Abramoff, an eye doctor and computer scientist at the University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics, has been developing an AI for diagnosing retinal disease for several years and is CEO of a spinoff startup called IDx Technologies, which has collaborated with IBM Watson. Abramoff has been a cheerleader for health-care AI in the past, but he also cautions against a rush, warning of a backlash if people have bad experiences with AI. “I’m so glad that Google shows they’re willing to look into the actual workflow in clinics,” he says. “There is much more to health care than algorithms.”
Abramoff also questions the usefulness of comparing AI tools with human specialists when it comes to accuracy. Of course, we don’t want an AI to make a bad call. But human doctors disagree all the time, he says—and that’s fine. An AI system needs to fit into a process where sources of uncertainty are discussed rather than simply rejected.
Get it right and the benefits could be huge. When it worked well, Beede and her colleagues saw how the AI made people who were good at their jobs even better. “There was one nurse that screened 1,000 patients on her own, and with this tool she’s unstoppable,” she says. “The patients didn’t really care that it was an AI rather than a human reading their images. They cared more about what their experience was going to be.”
Correction: The opening line was amended to make it clear not all countries are being overwhelmed.
Deep Dive
Artificial intelligence
Large language models can do jaw-dropping things. But nobody knows exactly why.
And that's a problem. Figuring it out is one of the biggest scientific puzzles of our time and a crucial step towards controlling more powerful future models.
Google DeepMind’s new generative model makes Super Mario–like games from scratch
Genie learns how to control games by watching hours and hours of video. It could help train next-gen robots too.
What’s next for generative video
OpenAI's Sora has raised the bar for AI moviemaking. Here are four things to bear in mind as we wrap our heads around what's coming.
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from
MIT Technology Review
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.