No One Knows How Much Cybercrime Really Costs
Before the Grum botnet of several hundred thousand compromised computers was taken down by law enforcement in 2012, it was responsible for sending out 18 billion spam messages per day, mostly hawking pharmaceuticals such as Viagra.
Grum was earning its operators nearly $3 million a year for pushing drug ads, but far more impressive were the indirect costs it imposed: it was believed responsible for nearly 20 percent of the world’s spam, which researchers at Microsoft and Google say costs the world $20 billion a year on things like e-mail filtering and storage.
The case of Grum is unusual in that the finances of spam are relatively well understood, making it possible to do a cost-benefit analysis of actions taken to stop it. That’s not the case with other threats, such as data breaches that feed personal information to the black market.
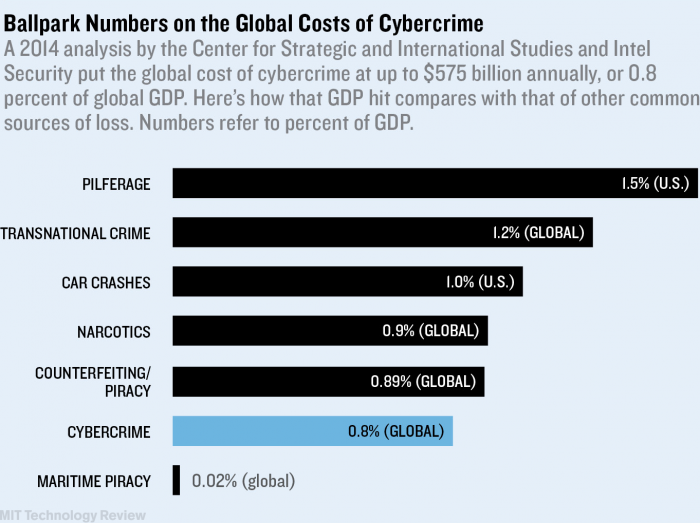
Although it’s clear that cybercrime imposes real and sizable costs on society, fine-grained data is generally hard to come by.
“Many of the private-sector reports are basically marketing brochures from organizations with a strong interest in scaremongering,” says Ross Anderson, a professor of security engineering at the University of Cambridge.
And law enforcement agencies and police don’t have good statistics on the incidence and costs of cybercrime because they have not updated their operations for the Internet era as well as criminals have, he says. A European Union research project recently concluded that a lack of clear figures on costs was preventing companies as well as governments and law enforcement from making good decisions about security.
“If data is patchy or unverifiable, then it is likely that businesses will either waste money or not spend any at all, leaving themselves and consumers vulnerable to attack,” says Jart Armin, a founder of the security company CyberDefcon, who is involved with the CyberROAD project behind the E.U. report.
Anderson and colleagues at Cambridge are in the process of setting up a new research center that could help clear up that confusion. The Cambridge Cloud Cybercrime Center will operate as a kind of clearinghouse for data from major companies—data that can be mined to discover the patterns of criminal activity. “We’ve got to be able to measure cybercrime to be effective in doing anything about it,” says Anderson.
Talks are under way with Google, Yahoo, and others interested in donating data.
“For the first time we’re going to be able to look at stuff at scale,” says Anderson. He hopes that the new resource will produce insights into the patterns and costs of cybercrime that could allow far more informed responses.
Keep Reading
Most Popular
Large language models can do jaw-dropping things. But nobody knows exactly why.
And that's a problem. Figuring it out is one of the biggest scientific puzzles of our time and a crucial step towards controlling more powerful future models.
How scientists traced a mysterious covid case back to six toilets
When wastewater surveillance turns into a hunt for a single infected individual, the ethics get tricky.
The problem with plug-in hybrids? Their drivers.
Plug-in hybrids are often sold as a transition to EVs, but new data from Europe shows we’re still underestimating the emissions they produce.
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from
MIT Technology Review
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.