Best of 2014: First Graphene Audio Speaker Easily Outperforms Traditional Designs
Most loudspeakers work using a diaphragm that creates pressure waves in air by mechanically vibrating. “For human audibility, an ideal speaker or earphone should generate a constant sound pressure level from 20 Hz to 20 kHz, i.e. it should have a flat frequency response,” say Qin Zhou and Alex Zettl who are both at the University of California, Berkeley.
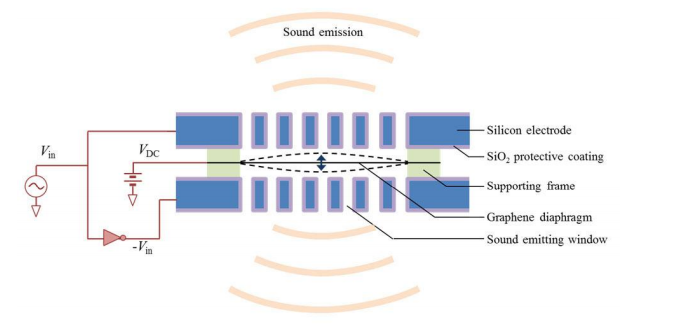
Today, these guys unveil an earphone-sized speaker that more or less matches this requirement. What’s unusual about this speaker is that the diaphragm is made from a few layers of graphene, the carbon chicken-wire material that is revolutionizing everything from transistor design to particle physics experiments.
Keep Reading
Most Popular
Large language models can do jaw-dropping things. But nobody knows exactly why.
And that's a problem. Figuring it out is one of the biggest scientific puzzles of our time and a crucial step towards controlling more powerful future models.
How scientists traced a mysterious covid case back to six toilets
When wastewater surveillance turns into a hunt for a single infected individual, the ethics get tricky.
The problem with plug-in hybrids? Their drivers.
Plug-in hybrids are often sold as a transition to EVs, but new data from Europe shows we’re still underestimating the emissions they produce.
Google DeepMind’s new generative model makes Super Mario–like games from scratch
Genie learns how to control games by watching hours and hours of video. It could help train next-gen robots too.
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from
MIT Technology Review
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.