Harvesting Heat
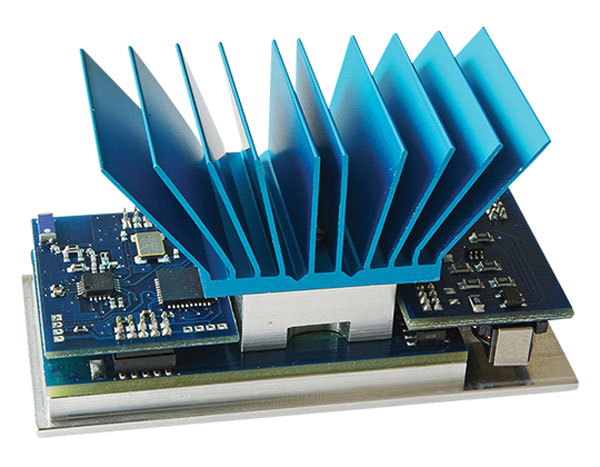
The TE-Power Node uses any source of thermal energy to drive a wireless transceiver, storing power in a thin-film battery. The Node is a test bed for designers looking to build the next generation of sensor networks, in which the sensors power themselves by harvesting energy from the environment. The battery stores the power that trickles in from sources such as a warm industrial exhaust pipe and then releases the accumulated energy in a pulse powerful enough to operate the radio. A 10 °C difference in temperature produces enough electricity to transmit 13 bytes of information per second.
Product: TE-Power Node
Cost: $637
Availability: Now
Source: www.micropelt.com
Companies: Micropelt and STMicroelectronics
Keep Reading
Most Popular
Large language models can do jaw-dropping things. But nobody knows exactly why.
And that's a problem. Figuring it out is one of the biggest scientific puzzles of our time and a crucial step towards controlling more powerful future models.
The problem with plug-in hybrids? Their drivers.
Plug-in hybrids are often sold as a transition to EVs, but new data from Europe shows we’re still underestimating the emissions they produce.
Google DeepMind’s new generative model makes Super Mario–like games from scratch
Genie learns how to control games by watching hours and hours of video. It could help train next-gen robots too.
How scientists traced a mysterious covid case back to six toilets
When wastewater surveillance turns into a hunt for a single infected individual, the ethics get tricky.
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from
MIT Technology Review
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.